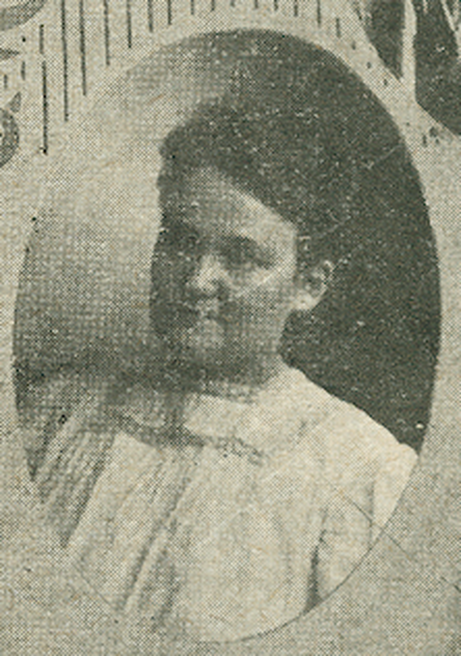Outstanding Resilience
Contributed to the Success
of Utah's Deaf Women's History
Contributed to the Success
of Utah's Deaf Women's History
Compiled & Written by Jodi Becker Kinner
Edited by Valerie G. Kinney
Published in 2020
Updated in 2024
Edited by Valerie G. Kinney
Published in 2020
Updated in 2024
Author's Note
As a Deaf feminist who is passionate about Women's Studies, I wanted to highlight the remarkable resilience of Utah's Deaf women. Despite facing marginalization in various aspects of life, including social, economic, professional, and political areas, these women have not only lived fulfilling and productive lives but have also achieved educational and career milestones that are truly admirable.
When writing about individuals for our history website, I choose to use their first name to acknowledge all individuals who contribute to and advocate for our community's causes. Our patriarchal culture often expects to recognize women's advocacy, contributions, and achievements using their husbands' last names instead of their own. However, in the spirit of inclusivity, equality, and recognizing each individual's unique identity, I have decided to use their first names throughout the website. This decision reaffirms our commitment to these values and highlights the significant role of women's advocacy in our community.
Our organization, previously known as the Utah Association for the Deaf, changed its name to the Utah Association of the Deaf in 2012. The association was known as the Utah Association of the Deaf from 1909 to 1962. The association changed its name to the Utah Association for the Deaf in 1963. Finally, in 2012, the association reverted to its previous name, the Utah Association of the Deaf. When writing the history website, I use both "of" and "for" to reflect the different eras of the association's history.
Thank you for your interest in reading 'Outstanding Resilience Contributed to the Success of Utah's Deaf Women's History.'
Enjoy!
Jodi Becker Kinner
When writing about individuals for our history website, I choose to use their first name to acknowledge all individuals who contribute to and advocate for our community's causes. Our patriarchal culture often expects to recognize women's advocacy, contributions, and achievements using their husbands' last names instead of their own. However, in the spirit of inclusivity, equality, and recognizing each individual's unique identity, I have decided to use their first names throughout the website. This decision reaffirms our commitment to these values and highlights the significant role of women's advocacy in our community.
Our organization, previously known as the Utah Association for the Deaf, changed its name to the Utah Association of the Deaf in 2012. The association was known as the Utah Association of the Deaf from 1909 to 1962. The association changed its name to the Utah Association for the Deaf in 1963. Finally, in 2012, the association reverted to its previous name, the Utah Association of the Deaf. When writing the history website, I use both "of" and "for" to reflect the different eras of the association's history.
Thank you for your interest in reading 'Outstanding Resilience Contributed to the Success of Utah's Deaf Women's History.'
Enjoy!
Jodi Becker Kinner
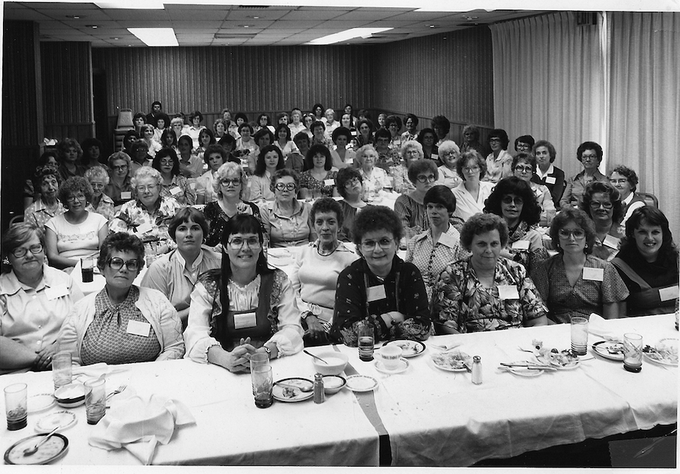
Deaf Women's Conference in Utah
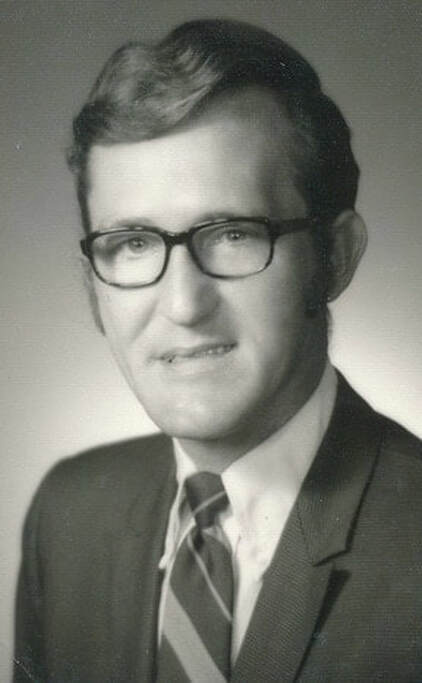
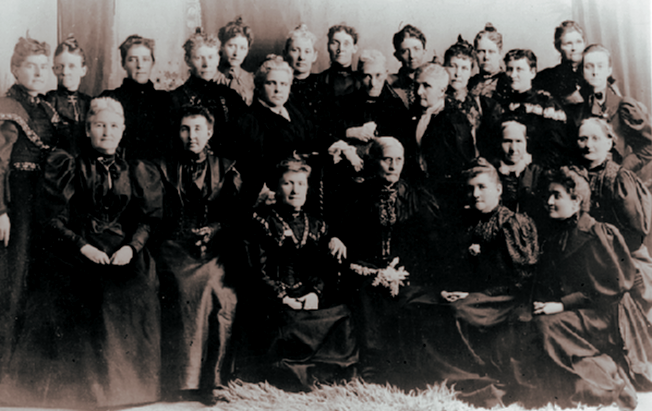
The Deaf Women's Conference was held on October 6th, 1979, at the International Dunes Hotel in Salt Lake City, Utah. Under the leadership of president W. David Mortensen, also known as Dave, the Utah Association for the Deaf sponsored the event.
The conference was planned by a committee consisting of Lois Jones as the chairperson, Celia May Laramie Baldwin, Darlene Stewart Cochran, and Ilene Coles Kinner. Over 80 women aged 18 to 80 were in attendance (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980).
A Deaf Advocate for Women's Rights
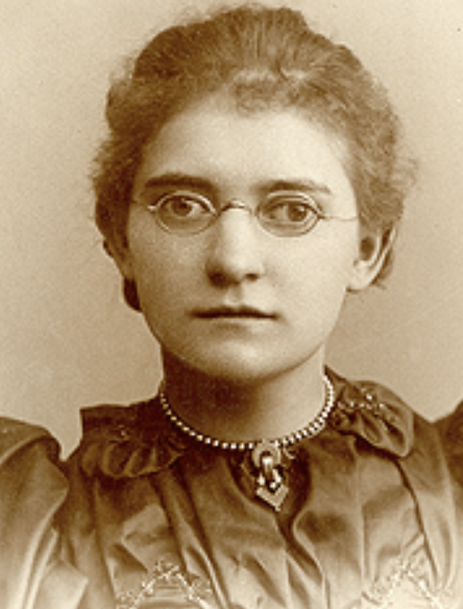
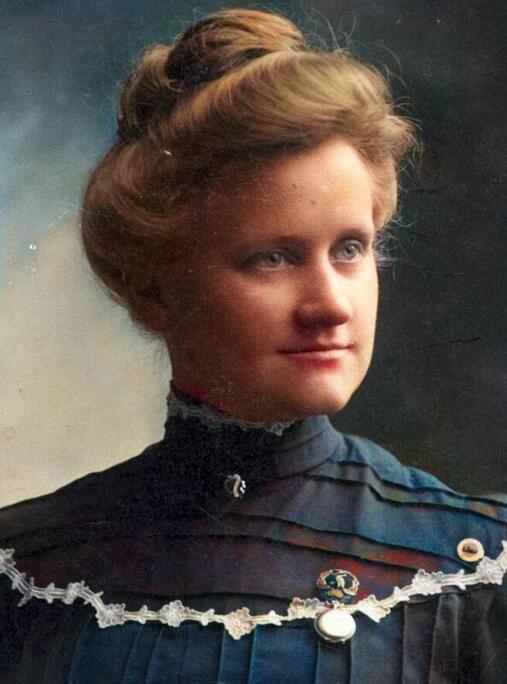
Dr. Gertrude Scott Galloway, a champion of Deaf women's rights and the first female president of the National Association of the Deaf, delivered a keynote address to the audience during the conference. In her speech, she highlighted the importance of women's rights and how they affect various areas, such as credit cards, salaries, and surnames. She also mentioned Agatha Tiegel Hanson, who was the first female graduate of Gallaudet College in 1893 and cited her graduation speech, "New Horizons For Deaf Women," which was written even before Women's Suffrage (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980).
New Horizons For Deaf Women
"Women should be free as the air to learn what she will and do devote her life to whatever vocation seems good to her…It is true that we have made a start in the right direction. But that start has been made very recently, and it is too early to pass sentence on the results."
~Agatha Tiegel Hanson, 1893~
~Agatha Tiegel Hanson, 1893~
Agatha Tiegel Hanson was the first female
graduate and valedictorian of Gallaudet College and early champion of both Deaf & Women's rights.
graduate and valedictorian of Gallaudet College and early champion of both Deaf & Women's rights.
Workshops at the
Deaf Women's Conference
Deaf Women's Conference
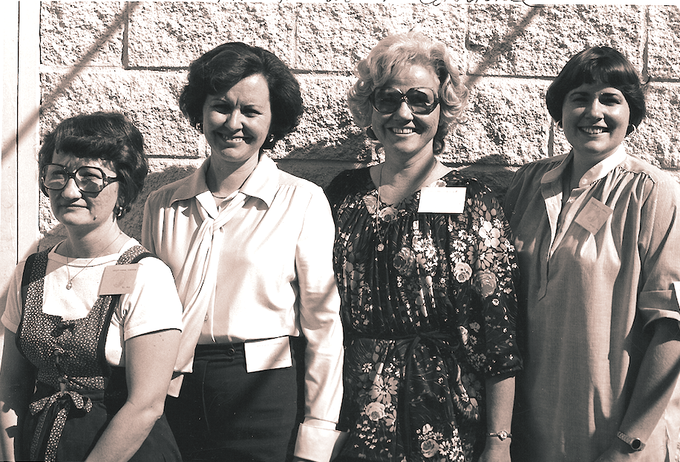
The workshops were conducted by Beth Ann Campbell, an esteemed local interpreter who was also a Child of Deaf Adults (CODA), and Nancy R. Rarus, a passionate advocate for Deaf Rights. Beth Ann discussed topics relevant to everyone, such as sex, family, and money. Meanwhile, Nancy offered her great understanding of leadership among women. She also focused her presentation on the Utah Community Center for the Deaf, a proposal that gained momentum during the 1980 Utah Legislative session (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980).
The conference, a resounding success, left a positive imprint on the attendees, igniting discussions about a potential women's conference in the coming year. The transformative effect of the conference was evident when one husband shared that his wife returned with a newfound sense of happiness, prompting him to pledge his unwavering support for her attendance, even if it meant paying $9.00 each time! (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980).
Since Agatha Tiegal Hanson's groundbreaking Gallaudet speech in 1893, women's progress and opportunities have been steadily advancing, and this trend continues today. While acknowledging the progress, we remain committed to achieving equal opportunities for women and girls.
The conference, a resounding success, left a positive imprint on the attendees, igniting discussions about a potential women's conference in the coming year. The transformative effect of the conference was evident when one husband shared that his wife returned with a newfound sense of happiness, prompting him to pledge his unwavering support for her attendance, even if it meant paying $9.00 each time! (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980).
Since Agatha Tiegal Hanson's groundbreaking Gallaudet speech in 1893, women's progress and opportunities have been steadily advancing, and this trend continues today. While acknowledging the progress, we remain committed to achieving equal opportunities for women and girls.
A Female Symbol
1994 Deaf Women's
Conference in Utah
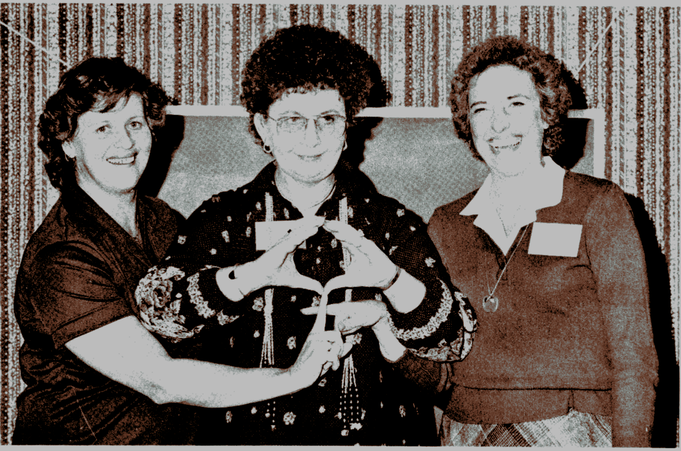
The Deaf Women's Conference took place at Salt Lake Community College on October 21–21, 1994, fifteen years later. Kristi Mortensen, a local Deaf feminist, chaired the conference with the theme "Towards the 21st Century: An Exciting Journey." The keynote speaker was Dr. Barbara Brauer, a pioneer in Deaf Mental Health. Dr. Petra M. Horn-Marsh, a Deaf Bilingual advocate, also presented the history of Deaf women's struggles and accomplishments. During the workshop sessions, Dr. Brauer gave a talk on "Women and Violence," and Dr. Lawrence Fleischer, a Deaf Studies professor at California State University, Northridge, presented "The Enhanced Image of a Deaf Woman: Amee Mathews.
Women Viewed as a Marginalized Group
Women, despite outnumbering men in college and the workforce, are still considered a marginalized group. Particularly, Deaf women endure further marginalization and potential double discrimination (The Deaf American, February 6, 1980). Unfortunately, women generally experience marginalization in education, social, economic, professional, and political spheres. Utah ranks lowest in the nation in terms of gender equality, with a low representation of women in politics, a gender pay gap, and a disparity between men and women in obtaining a college education. Despite these challenges, women across the country are working to advocate, educate, and promote gender equality.
Deaf Women Face Double Barriers
Deaf women face a range of challenges in various aspects of their lives, such as education, socialization, economics, professionalism, and politics. Despite these obstacles, many Deaf women have led fulfilling and productive lives similar to those of their hearing counterparts. Some have overcome significant hurdles and accomplished great things in their education and careers. It is crucial to acknowledge and reward these women for their achievements. The website presents 'Biographies of Prominent Utah Deaf Women' who have accomplished great things, highlighting the importance of recognizing and celebrating their accomplishments.
Utah Deaf Women Who Made
a Difference in the Deaf Community
a Difference in the Deaf Community
During the late 1800s and early 1900s, many women in Utah were progressive in their education and careers while advocating for their political goals, even while practicing polygamy. These women were also involved in various fields, such as activism, medicine, academia, writing, and politics (Brooks, Steenblik & Wheelwright, 2016). The suffrage movement, a pivotal moment in women's history, significantly shaped their ambitions. This influence extended to Deaf women in Utah.
Elizabeth DeLong, the First Female President
of the Utah Association of the Deaf
of the Utah Association of the Deaf
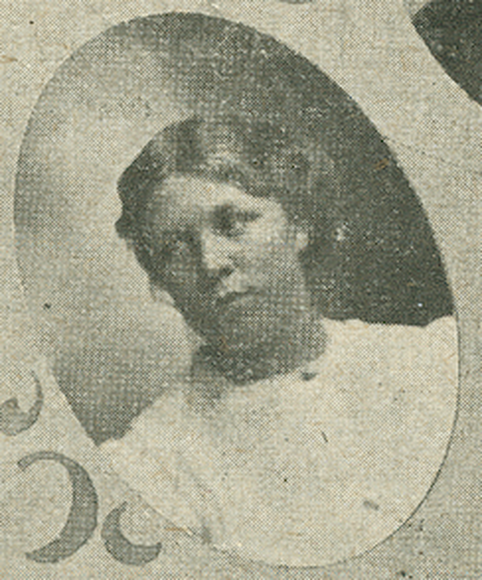
In 1909, Elizabeth DeLong, also known as Libbie, made history by defeating two male Deaf candidates, becoming the first female Deaf president of the Utah Association of the Deaf, an advocacy organization for accessibility and civil rights of the Utah Deaf community. Additionally, she became the first female Deaf president of a state chapter association of the National Association of the Deaf in the United States. Her victory over two Deaf male candidates in the election, despite the societal barriers, was a significant achievement. Women did not have the right to vote until the 19th Amendment was ratified in 1920, and the National Association of the Deaf also did not allow Deaf women members to vote in their elections until 1964. Libbie's remarkable accomplishment was a testament to her perseverance, likely inspired by her involvement in Gallaudet's O.W.L.S. presidential election in 1901, a secret society for women now known as Phi Kappa Zeta. Her active participation in Utah's early suffrage movement also fueled her educational, political, and spiritual aspirations. Libbie served as president of the Utah Association of the Deaf from 1909 to 1915, delivering a speech advocating for women's suffrage at the end of her second term as president. This speech highlighted her commitment to advocating for women's rights and her role as a trailblazer for Deaf women in leadership positions. Her support for women's suffrage, as well as her significant contributions to the Utah Deaf community and the women's rights movement, continue to serve as inspiration today, underscoring the enduring impact of her work.
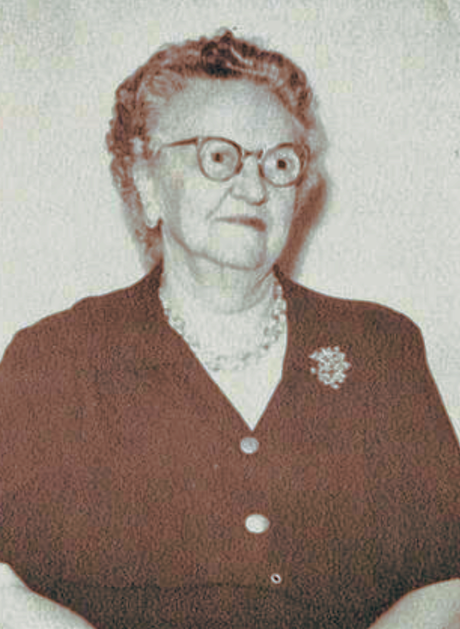
Emma M. Emmertson, as her grandson Don Jorgenson II revealed in an interview with Carolyn Jorgenson, was a suffragette who actively participated in the Women's Suffrage Movement from the late 19th to the early 20th century. This movement was a significant social and political campaign that sought to secure voting rights for women. Emma's granddaughter, Kristan Jorgensen, also described Emma as a very strong woman on FamilySearch.org.
Notably, Utah's women's suffrage campaign, a local movement crucial in influencing history, had a big impact on Emma's involvement in it. This movement, which successfully granted women the right to vote in Utah in 1870, also considerably influenced Elizabeth DeLong, the first female president of the Utah Association of the Deaf. Emma was inspired by the courage and determination of these women, which fueled her own activism.
Notably, Utah's women's suffrage campaign, a local movement crucial in influencing history, had a big impact on Emma's involvement in it. This movement, which successfully granted women the right to vote in Utah in 1870, also considerably influenced Elizabeth DeLong, the first female president of the Utah Association of the Deaf. Emma was inspired by the courage and determination of these women, which fueled her own activism.
In 1910, Mary Wooslayer, a Deaf woman, made history by becoming the first female Deaf student to graduate from the University of Utah with a bachelor's degree. Maud May Babcock, a member of the Utah School for the Deaf Board of Trustees and a faculty member at the University of Utah, sponsored Mary during her time at the university (Mary Woolslayer Photograph Collection, 1890). The state's early efforts to promote education and employment opportunities for women, along with her connection with Maud May Babcock, likely influenced Mary's decision to pursue higher education at the University of Utah, where she graduated in 1916. Similarly, Emma M. Emmertson enrolled at the University of Utah the following year, in 1911, and graduated in 1917. After completing their college education, both Mary and Emma went on to teach in the state schools for the deaf.
Gallaudet College, between 1864 and 1887, denied Deaf women admission (US History Encyclopedia: Gallaudet University). Similarly, the National Fraternal Society of the Deaf, established in 1901 as a Deaf-owned and operated insurance organization, provided insurance to Deaf men but initially denied full membership and admission to women. Among these women was Justina Wooldridge Keeley, who discovered NFSD for the Utah Deaf community while visiting her home state of Missouri. Despite these obstacles, women, including Justina, persevered. Their efforts culminated in a significant victory in 1951, during the NFSD convention in Chicago, Illinois. After fifty years of struggle, women like Justina finally received regular insurance membership in this year, marking a significant turning point. This victory allowed women to receive regular insurance membership and join the organization for the first time, a momentous occasion in the history of Deaf culture and gender equality (Records of the National Fraternal Society of the Deaf, 1900–2006).
Did You Know?
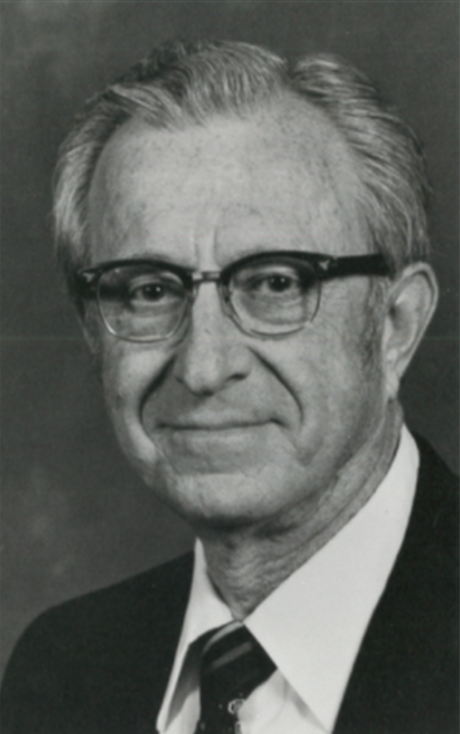
In July 1964, as Dr. Robert G. Sanderson, our Utah prominent figure, was to be elected president of the National Association of the Deaf, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was passed, marking a momentous occasion when the NAD granted Deaf women the right to vote. This was a significant step in promoting inclusivity and equality within the NAD. After the Voting Rights Act of 1965 was passed, the National Association of the Deaf allowed Black Deaf people to join and vote in the NAD in 1965, further enhancing this commitment. Prior to 1965, the National Association of the Deaf did not give female members the right to vote, nor did it give Black individuals any right to membership. These changes were an important milestone in creating a more inclusive community for all Deaf individuals, regardless of ethnicity, gender, or sexual orientation. The new change also marked a historic turning point in the NAD's history, signifying a shift towards inclusivity and equality. It also highlighted the unity and collaboration within the National Association of the Deaf, a testament to the collective effort of its members and their shared vision of a more inclusive future. This shared vision makes us all feel hopeful and optimistic about the future of this community.
Kim Lucas, the Second Female President
of the Utah Association of the Deaf
of the Utah Association of the Deaf
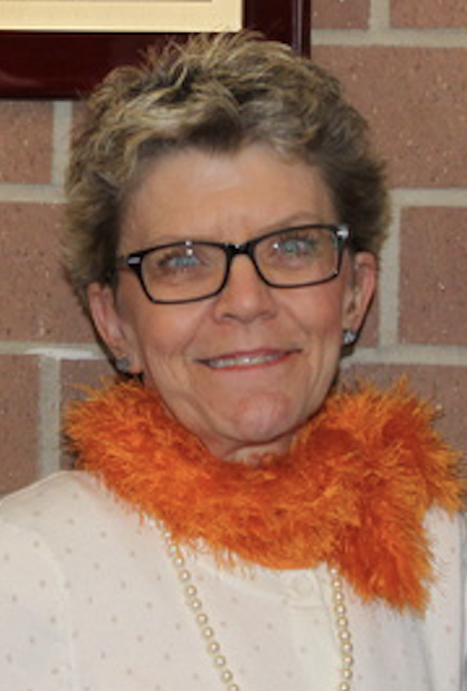
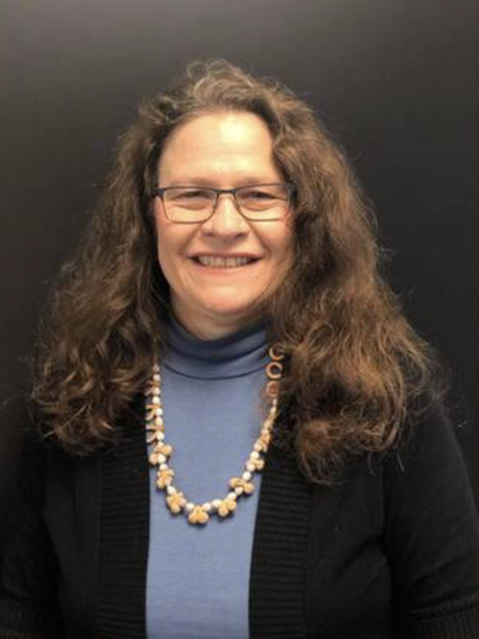
In 2019, Kim Lucas made history by becoming the second woman to serve as president of the Utah Association of the Deaf, breaking a streak of 104 years during which only men held the position. The first female president, Elizabeth Delong, completed her term in 1915, making Kim's presidency a significant milestone for the organization. Her journey to the presidency was a testament to the progressiveness and inclusivity of the Utah Association of the Deaf, which supported her every step of the way and paved the way for greater diversity in leadership. Notably, Kim is also the first queer president to lead the Utah Association of the Deaf, marking a historic moment in multiple ways and inspiring hope for the future of women's leadership and representation in the Deaf Queer community.
From there, Kim steered the Utah Association of the Deaf towards emphasizing social justice concerns, leading to the formation of regular gatherings such as Queer ASL Utah and Utah Deaf Womxn. Meanwhile, under the supervision of the Department of Workforce Services, the DSDHH cut ties with the Utah Association of the Deaf for the first time in 2019 but continued providing activities for the Deaf, Hard of Hearing, and DeafBlind communities. UAD also supported the relaunch of Deaf Night Out. Kim served as president for four and a half years. Her presidency came to an end because of the bylaws. Her presidential leadership was much appreciated and well respected.
From there, Kim steered the Utah Association of the Deaf towards emphasizing social justice concerns, leading to the formation of regular gatherings such as Queer ASL Utah and Utah Deaf Womxn. Meanwhile, under the supervision of the Department of Workforce Services, the DSDHH cut ties with the Utah Association of the Deaf for the first time in 2019 but continued providing activities for the Deaf, Hard of Hearing, and DeafBlind communities. UAD also supported the relaunch of Deaf Night Out. Kim served as president for four and a half years. Her presidency came to an end because of the bylaws. Her presidential leadership was much appreciated and well respected.
For the first time since 1909, the Utah Association of the Deaf has achieved a significant milestone with two female presidential officers: Kim Lucas as president and Ashli-Marie Grant Mayo as vice president. This marks a significant step towards gender equality and diversity in the leadership of our organization.
Utah Deaf Womxn Group
The Utah Deaf Womxn Group was established in 2019 by Kim Lucas, president of the Utah Association of the Deaf, and Ashli-Maire Grant, vice president of the Utah Association of the Deaf, along with two advocates, Emisha Sill and me. The group's goal is to promote the diverse lives of Deaf womxn, regardless of their gender, race, and sexual identities, by empowering and enriching them. The group aims to bring together Deaf womxn in a supportive environment where they can socialize and learn from each other.
The Utah Deaf Womxn Group operates under the umbrella of the Utah Association of the Deaf. As mentioned earlier, this group was created to address the marginalization of Deaf womxn educationally, socially, economically, professionally, and politically. Utah is one of the worst states in the nation for womxn, with challenges such as the gender inequality pay gap, fewer womxn completing their college education, and difficulties in climbing the economic ladder. Deaf womxn, in particular, face double oppression due to communication barriers.
The Utah Deaf Womxn Group is committed to addressing gender inequality, highlighting the achievements of female and queer leaders, and developing strategies to promote leadership and service within the Utah Deaf community. The group also aims to improve the quality of life for all community members by addressing political, legal, and cultural issues that womxn, especially Deaf womxn, face in Utah and nationally. By collaborating, the group can make a significant impact on the lives of womxn in the community.
The Utah Deaf Womxn Group operates under the umbrella of the Utah Association of the Deaf. As mentioned earlier, this group was created to address the marginalization of Deaf womxn educationally, socially, economically, professionally, and politically. Utah is one of the worst states in the nation for womxn, with challenges such as the gender inequality pay gap, fewer womxn completing their college education, and difficulties in climbing the economic ladder. Deaf womxn, in particular, face double oppression due to communication barriers.
The Utah Deaf Womxn Group is committed to addressing gender inequality, highlighting the achievements of female and queer leaders, and developing strategies to promote leadership and service within the Utah Deaf community. The group also aims to improve the quality of life for all community members by addressing political, legal, and cultural issues that womxn, especially Deaf womxn, face in Utah and nationally. By collaborating, the group can make a significant impact on the lives of womxn in the community.
Deaf Women United
Deaf Women United is an organization with a mission to empower and elevate the status of Deaf women. We strive to raise awareness of the inequalities that still exist and celebrate female leaders' accomplishments. We also recognize the history of unequal treatment of women and aim to develop leadership skills and increase service to the Deaf Women's community, thus improving their lives.
If you'd like to support our Deaf Women's community, please sign up for the Deaf Women United newsletter at http://www.dwu.org.
If you'd like to support our Deaf Women's community, please sign up for the Deaf Women United newsletter at http://www.dwu.org.
Accolades of the Early Utah
Deaf & Non-Deaf Women's History
Check out the "Outstanding Contributions in the Early History of Utah's Deaf and Non-Deaf Women" webpage to learn more about women's history in Utah.
References
Brooks, Joanna, Steenblik Rachel Hunt and Wheelwright, Hannah. "Mormon Feminism Essential Writing." Oxford University Press, 2016.
Gallaudet University Library Deaf Collections and Archives, "Records of National Fraternal Society of the Deaf, 1900-2006."
“Locals.” The Buff and Blue, vol. 10, no. 1 (October 1901), p. 29.
Mary Woolslayer Photograph Collection. (1890). J. Willard Marriot Library, University of Utah. Collection Number UU_P0669.
The Deaf American Vol. 32 No. 06 February 1980. https://archive.org/details/TheDeafAmerican3206February1980/page/n9/mode/2up
Gallaudet University Library Deaf Collections and Archives, "Records of National Fraternal Society of the Deaf, 1900-2006."
“Locals.” The Buff and Blue, vol. 10, no. 1 (October 1901), p. 29.
Mary Woolslayer Photograph Collection. (1890). J. Willard Marriot Library, University of Utah. Collection Number UU_P0669.
The Deaf American Vol. 32 No. 06 February 1980. https://archive.org/details/TheDeafAmerican3206February1980/page/n9/mode/2up